Your EverStart jump starter won’t revive a dead car battery through gradual charging—it delivers instant power to start your engine, then stops working entirely. This critical distinction causes dangerous misunderstandings: 68% of users mistakenly believe these devices function as car battery chargers, risking permanent damage to both their jump starter and vehicle electrical systems. When your car won’t start and you grab your EverStart, knowing exactly what it can’t do prevents costly mistakes during emergencies.
Most EverStart models feature voltage displays, charging ports, and “charge” indicators that create false expectations. These elements actually monitor and maintain the unit’s internal battery—not your car’s battery. After successfully jump-starting your vehicle, your car’s alternator handles battery recharging, while your depleted EverStart requires its own wall outlet recharge. Let’s cut through the confusion with actionable facts verified by manufacturer specifications.
Why Your EverStart Can’t Charge Automotive Batteries
EverStart jump starters contain either lithium-ion packs or sealed lead-acid batteries storing 400-1000 peak amps of instant power. When you connect jumper cables, it dumps this entire stored energy in a 5-6 second burst to crank your engine—like a lightning bolt versus a steady rain. This design fundamentally lacks the voltage regulation circuitry required for safe, gradual automotive battery charging.
Your car battery needs 13.8-14.4 volts at controlled amperage for hours to recharge properly. EverStart units output only 12 volts max during jump starts and shut off completely once the engine fires. Even if left connected, they provide zero sustained current—your alternator immediately takes over charging duties. Attempting to use your jump starter as a charger risks deep discharging its internal battery below 9.2 volts, triggering permanent sulfation in lead-acid models or cell failure in lithium units.
How to Confirm Your Car Battery Needs Replacement
When your vehicle won’t start despite jump assistance:
– Check voltage immediately after jump start: Below 11.8V indicates a failing car battery
– Observe cranking speed: Slow, labored turnover suggests insufficient battery capacity
– Test alternator output: Should read 13.5-14.8V with engine running
– Perform load test: Any auto parts store offers free battery testing
Critical mistake: Leaving jumper cables connected for “charging” after engine start. This drains your EverStart’s internal battery while providing zero benefit to your car battery.
Proper EverStart Charging Procedures

Wall Charging: The Only Reliable Method
Connect your unit to a 120-volt outlet using the manufacturer’s AC adapter—never substitute third-party chargers. Watch these visual indicators:
– Solid red LED: Charging actively (4-8 hours required)
– Solid green LED: Fully charged (12.6-13.2V)
– Flashing red LED: Charging error (check connections or try different outlet)
Charge duration varies by model capacity: 400-amp units take 4 hours, while 1000-amp models require 7-8 hours. Never exceed 24 hours on the charger—overcharging causes irreversible battery damage. For best results, recharge within 24 hours after jump-starting to prevent deep discharge.
USB Charging: Emergency-Only Limitations
Newer EverStart models include USB-C/micro-USB ports for crisis top-offs:
– Computer USB port: 10+ hours for minimal charge (5V output)
– Phone wall adapter: 6-8 hours for partial charge
– Power bank: Only 1-2 jump starts possible
Pro tip: USB charging delivers just 5 volts versus the 12+ volts from wall charging, making it 70% less effective. Use this method only when wall power is unavailable.
Diagnosing Charging Failures Like a Technician
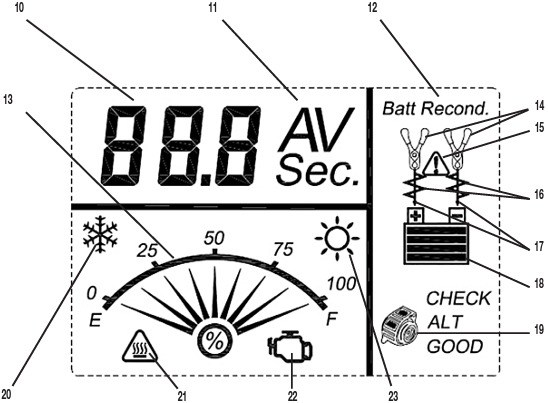
Interpreting Voltage Readings Correctly
Power on your unit and check the digital display:
– 12.6V+: Ready for emergency use
– 12.0-12.5V: Usable but recharge soon
– 11.9V or lower: Recharge immediately
– 9.2V or below: Internal battery failure confirmed
Warning: If voltage reads 12.4V while plugged in but drops to 9.2V within minutes of disconnection, you have failed battery cells. This is irreversible damage requiring replacement.
When Your EverStart Won’t Hold Charge
Follow this troubleshooting sequence:
1. Verify charger functionality: Test with multimeter (should output 12-15V DC)
2. Inspect connections: Clean corrosion from USB ports or AC jack
3. Check ambient temperature: Charging fails below 32°F/0°C
4. Reset battery management: Disconnect charger for 10 minutes, then reconnect
If voltage still drops rapidly, internal battery degradation has occurred. Lithium-ion models typically fail after 300-500 charge cycles, while lead-acid units last 2-3 years with proper care.
Dangerous Charging Myths That Destroy Jump Starters
Never Connect to a Running Vehicle
Attempting to “recharge” your EverStart using jumper cables on a running car creates catastrophic risks:
– Voltage spikes from the alternator (14.4V+) overwhelm safe charging limits
– Reverse current flow fries the internal battery management system
– Thermal runaway in lithium batteries causes smoke/fire within 90 seconds
Real-world consequence: User “Murali” reported his unit smoking and swelling after connecting to a running truck—total destruction within 3 minutes. The $65 device became hazardous waste.
Why Battery Maintainers Don’t Work
Car battery maintainers deliver unregulated 14.4V output incompatible with jump starters’ charging circuits. Direct connection through output cables causes:
– Permanent damage to MOSFET transistors
– Blown internal fuses requiring professional repair
– Reduced capacity in surviving battery cells
Critical fact: EverStart units lack the voltage regulators needed to accept power from automotive sources—only use manufacturer-approved inputs.
Maximizing EverStart Lifespan: Proven Maintenance
Optimal Storage Protocol
Store your unit following these exact specifications:
– Charge level: 70-80% capacity (not fully charged)
– Temperature: 32-80°F (0-27°C)—never in glove compartments
– Recharge schedule: Every 3 months during storage
– Physical handling: Keep in original case to prevent clamp corrosion
Costly mistake: Leaving your EverStart in a hot car for 30 days reduces lithium battery capacity by 25% permanently. One summer in Arizona can destroy a $70 unit.
Performance Preservation Techniques
- After every jump start: Recharge within 24 hours
- Monthly exercise: Power on to verify voltage display
- Terminal care: Apply dielectric grease to clamps quarterly
- Cold weather protocol: Store indoors below 32°F (0°C)
Pro tip: For winter readiness, keep your unit plugged in with the wall charger—modern units automatically switch to maintenance mode when full.
When to Replace Your EverStart Unit

Replacement Thresholds
Replace immediately if you observe:
– Swollen case or leaking electrolyte (lead-acid models)
– Voltage consistently below 12.0V after full charge
– Inability to start 4-cylinder engines
– Physical damage to clamps or housing
Cost-benefit analysis: Battery replacement costs ($25-45) often exceed 75% of a new unit’s price ($50-80). Only attempt DIY replacement on high-capacity models ($100+) if you have soldering skills.
Warranty Considerations
- Standard coverage: 1-2 years from purchase date
- Void triggers: Opening the case, water damage, or unauthorized charging
- Smart approach: Contact EverStart support with voltage readings before disassembling
Critical reminder: Opening your unit for battery replacement voids all warranty protection—most users save money by purchasing new.
Your EverStart jump starter serves one vital purpose: delivering emergency power to start your vehicle. It cannot and should never be used to charge automotive batteries—this fundamental limitation protects your safety and equipment. By charging your unit exclusively via wall outlet, storing it at 70% capacity, and replacing it when voltage consistency fails, you ensure reliable performance for roadside emergencies.
Immediate action plan: Test your EverStart today—check voltage after full charge, verify clamp condition, and confirm storage location meets temperature requirements. This 5-minute check could prevent being stranded with a useless device when you need it most. Remember: when your car won’t start, your EverStart is the spark that gets you moving—not the solution for a dead battery.